Final MD exam 2022
Monday, May 30, 2022
Sunday, May 29, 2022
40 year old woman with multiple joint pains
A 40 year old woman, working as a tailor presented to our outpatient unit with the complaints of
Multiple joint pains since the past 7 years.
Present Illness:
A 40 year old woman was apparently asymptomatic 7 years back after which she started experiencing multiple joint pains. She reported that she first experienced right proximal interphalangeal joint pain 7 years back while she was working on the sewing machine. After 2 weeks she started to experience left proximal interphalangeal joint pain. Over the last 7 years, she started experiencing multiple joint pains - bilatered meta-carpophalangeal joint, bilateral elbow joint, bilateral wrist joint, cervival joint, bilateral knee joint, bilateral ankle joint pains. She reported early morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour which would be relieved on physical activity. She would experience these pains intermittently and would often be accompanied by swelling of the joint and would be relieved on taking pain medications. She reported that she developed bilateral little finger deformity 1 year back.
She however gave no history of fever, oral ulcers, rash, dryness of the skin, hair loss, any development of rash on exposure to sunlight, discouloration of skin on exposure to cold.
No other constitutional symptoms like fever, fatigue, weight loss.
Past History:
No other significant past history
Personal History:
She is happily married and a mother of 2 children. She has a good appetite, normal bowel and bladder movements.
Family History:
No significant family history
Provisional Diagnosis:
Chronic, multiple, symmetrical joint involvement, involvement of PIP & DIP joints - ? Rheumatoid Arthritis
Examination:
Pulse Rate: 75 beats per minute
Blood Pressure: 120/70mmhg
Respiratory Rate: 22 cycles per minute
Temperature: 98.6 F
No pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, lymphadenopathy, edema
General Examination:
Hair:
Normal hair distribution, normal texture, colour
Eyes:
No conjunctival injection, no erythema, no corneal lesions
Oral Cavity:
No mucosal ulcers
Nails:
No nail pitting, onycholysis, onychodystrophy
Skin:
No rash , ulcers over the skin, scaly lesions, dryness of skin, thickening of skin, no rash on sun exposed areas of the skin, no subcutaneous nodules
Spine:
No spinal deformity
Musculoskeletal System Examination:
Gait: Normal
Musculoskeletal system:
Upper limbs:
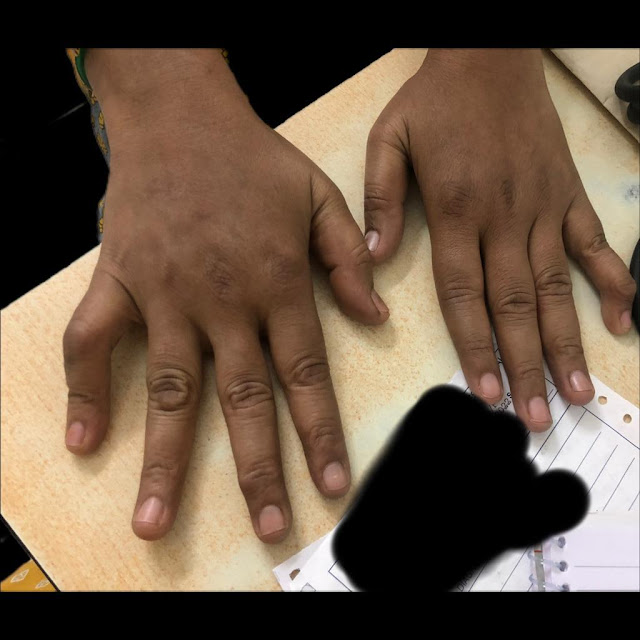
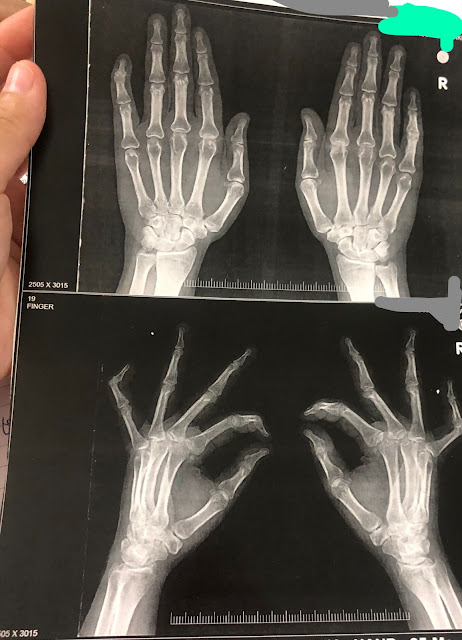
Boutenniere' or button hole deformity of the right little finger &
Swan neck deformity of the left little finger:
Saturday, May 28, 2022
22 year old woman with Generalized Anasarca and Facial Puffiness
A 22 year old woman presented to our outpatient unit with the complaints of
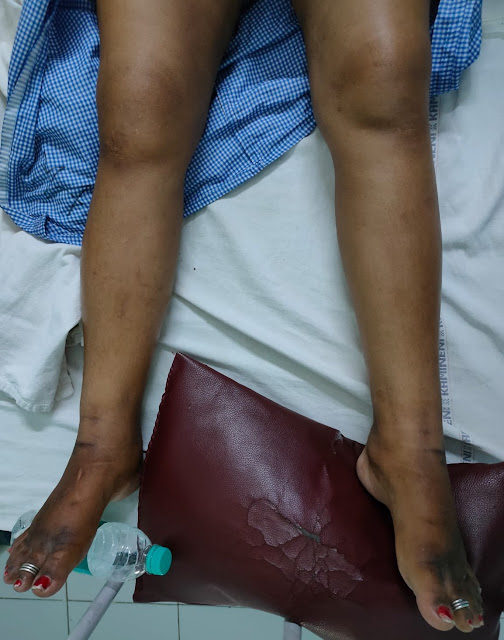
Bilateral lower limb swelling since 1 month
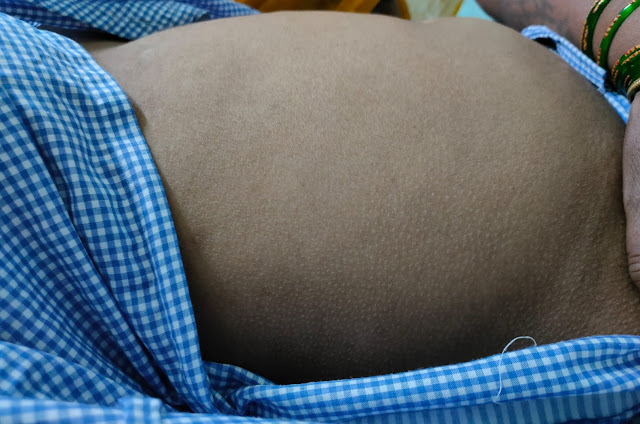
Facial puffiness since 1 month
Shortness of breath since 1 month
Reduced urine output since 1 week
History of present illness :
1 month back, she first noticed bilateral lower limb swelling, pitting type upto her ankles which gradually extended to her thighs. Following this she also developed facial puffiness, significantly around her eyes which alarmed her and she paid a visit to our hospital and was started on conservative medications. However her symptoms did not subside. She started experiencing dyspnea on exertion which gradually progressed to an extent that she found it difficult to even walk for a short distance. She reported frothing of urine, however she had no hematuria. She complaints of reduced urine output since 1 week.
She did not have any history of chest pain, palpitations, giddiness, sweating.
She denied any history of fever, sore throat, rash, joint pains. No history of drug intake or antibiotic usage.
Past History:
12 years back, she was diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus on visiting a local hospital for fever and body pains. She has been receiving insulin injections since then.
In 2018, she was admitted in a local hospital for slurred speech which eventually became normal on normalising her blood sugar levels.
Her father reported that she had to be readmitted 2-3 times there after with the same complaints of slurred speech and hyperglycaemia. She was started on Injection Human Insulin Mixtard 18 units in the morning and 12 units at night.
6 months back, she was diagnosed with Hypertension on routine follow up and was started on Tab Telma 40mg once daily.
4 months back, she had an abortion at 7 weeks of gestation since the fetal heart beat couldn’t be assessed.
Personal History:
She currently lives with her parents who work as daily wage laborers. She has 2 elder sisters, who are married. She studied till 10th standard. She was married 1 year back to a farmer, however they haven’t been living together ever since her miscarriage.
Her mother reported decreased appetite since the last 2 months. She has only been consuming only milk, once to twice a day along with chapatti once in a day.
Problem Representation:
1. Generalized Anasarca
2. Dyspnea on exertion
3. Reduced urine output
4. Uncontrolled blood sugars
Provisional Diagnosis:
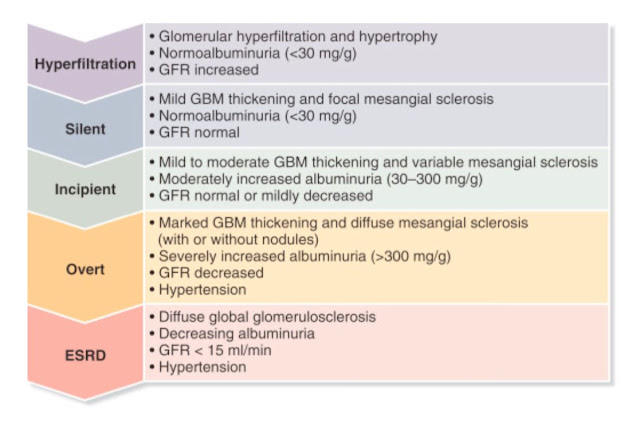
1. A 22 year old woman with significicant generalized anasarca, proteinruria and hypertension - Nephrotic Syndrome - ? Diabetic Nephropathy
2. Anemia secondary to ? chronic disease
3. Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus since 12 years
4. Hypertensive since 6 months
Clinical Examination:
General Examination:
Pulse Rate: 90 beats per minute, normal on volume, no radio-radial or radio-femoral delay
Blood Pressure: 150/70mmhg, right arm, supine posture
Respiratory Rate: 22 cycles per minute
Temperature: 98.6 F
Spo2: 98% on Room Air
GRBS: 260mg/dl
Height: 152.4 cm
Weight: 58 kgs
Body Mass Index: 23.2 kg/m
Waist circumference: 96 cms
Images from previous admission:
Current admission pictures:
Head to toe:
Hair: Normal colour and texture, No areas of hair loss.
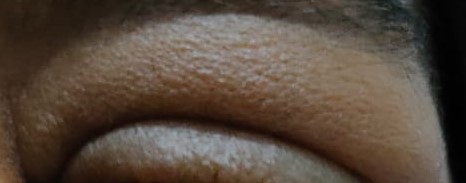
Eyes:
Pallor +
Periorbital edema +
Bilateral pterygium +
No cyanosis, icterus
Bilateral lower limb edema, comparatively reduced due to Hemodialysis
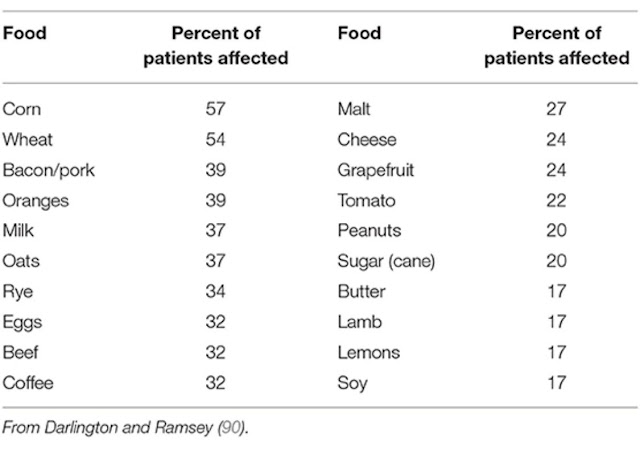
According to this the patients on intensive phase reduced risk of diabetic retinopathy, only 23 patients developed diabetic retinopathy and 91 patients on conventional therapy developed retinopathy.
-
A 40 year old woman, working as a tailor presented to our outpatient unit with the complaints of Multiple joint pains since the past 7 year...
-
A 22 year old woman presented to our outpatient unit with the complaints of Bilateral lower limb swelling since 1 month Facial puffiness si...


.jpeg)


.jpeg)

.jpeg)








.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)










.jpeg)




.jpeg)
.jpeg)


