A 40 year old woman, working as a tailor presented to our outpatient unit with the complaints of
Multiple joint pains since the past 7 years.
Present Illness:
A 40 year old woman was apparently asymptomatic 7 years back after which she started experiencing multiple joint pains. She reported that she first experienced right proximal interphalangeal joint pain 7 years back while she was working on the sewing machine. After 2 weeks she started to experience left proximal interphalangeal joint pain. Over the last 7 years, she started experiencing multiple joint pains - bilatered meta-carpophalangeal joint, bilateral elbow joint, bilateral wrist joint, cervival joint, bilateral knee joint, bilateral ankle joint pains. She reported early morning stiffness lasting for more than an hour which would be relieved on physical activity. She would experience these pains intermittently and would often be accompanied by swelling of the joint and would be relieved on taking pain medications. She reported that she developed bilateral little finger deformity 1 year back.
She however gave no history of fever, oral ulcers, rash, dryness of the skin, hair loss, any development of rash on exposure to sunlight, discouloration of skin on exposure to cold.
No other constitutional symptoms like fever, fatigue, weight loss.
Past History:
No other significant past history
Personal History:
She is happily married and a mother of 2 children. She has a good appetite, normal bowel and bladder movements.
Family History:
No significant family history
Provisional Diagnosis:
Chronic, multiple, symmetrical joint involvement, involvement of PIP & DIP joints - ? Rheumatoid Arthritis
Examination:
Pulse Rate: 75 beats per minute
Blood Pressure: 120/70mmhg
Respiratory Rate: 22 cycles per minute
Temperature: 98.6 F
No pallor, icterus, cyanosis, clubbing, lymphadenopathy, edema
General Examination:
Hair:
Normal hair distribution, normal texture, colour
Eyes:
No conjunctival injection, no erythema, no corneal lesions
Oral Cavity:
No mucosal ulcers
Nails:
No nail pitting, onycholysis, onychodystrophy
Skin:
No rash , ulcers over the skin, scaly lesions, dryness of skin, thickening of skin, no rash on sun exposed areas of the skin, no subcutaneous nodules
Spine:
No spinal deformity
Musculoskeletal System Examination:
Gait: Normal
Musculoskeletal system:
Upper limbs:
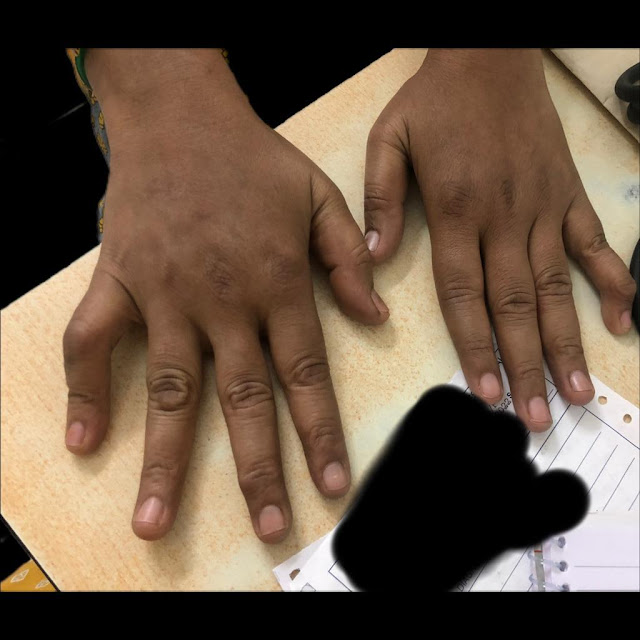
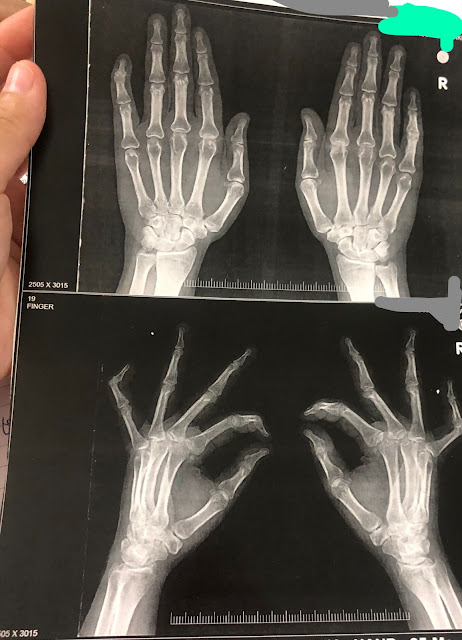
Boutenniere' or button hole deformity of the right little finger &
Swan neck deformity of the left little finger:
Prayer sign:
No tenderness or erythematous noted on examination of the joints
Restriction of joint motion noted only in the right PIP joint and left DIP joint
No restriction of other joint movements
Shoulder joint examination: No swelling or erythema of shoulder joints
No restriction of joint movement
Apprehension test negative - For looking for glenohumeral instability
No tenderness of knee & ankle joints
No joint restriction
Absent Achilles tendon swelling or tenderness
Absent Trendelenberg test
Negative Modified Schobers test: More than 15 cms
Other systems:
Respiratory System: No abnormality detected
Cardiovascular System: No abnormality detected
Abdomen: No abnormalities detected
Nervous System: No abnormalities detected
Provisional Diagnosis:
Multiple symmetrical polyarthritis with chronic duration of around 7 years and with signs of inflammation, involving PIP joints and MCP joints with sparing of DIP joints - Rheumatoid Arthitis
with no other system involvement.
Investigations:
Metabolic Profile - Normal
ESR: 20 mm/hr
CRP: Positive
RA factor: Positive
Diagnosis:
Multiple symmetrical joint involvement, chronic duration of more than 7 years- Rheumatoid arthritis
with an ACR - EULAR Criteria of 9
More than 10 joints involvement - 5, Serology - Score 2, Abnormal CRP - 1, More than 7 years of duration - 1
Discussion:
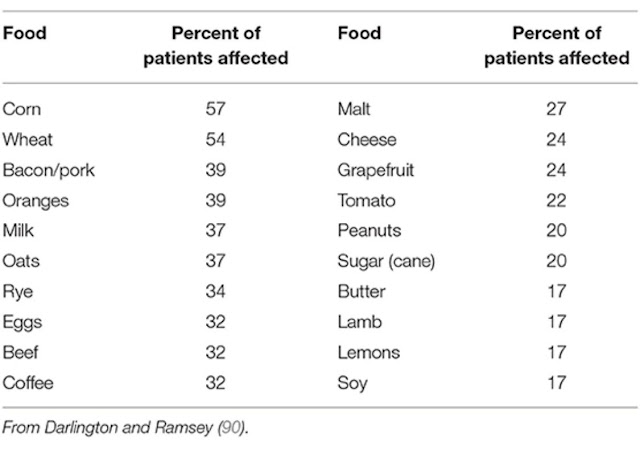
Darlington et al. used elimination and oral food challenge to identify foods capable of inducing symptoms in RA patients. Forty-eight patients undertook a 6-week elimination diet; forty-one were found to have foods that triggered symptoms.
Microbiome and Inflammation
The gut may play a key role in the pathophysiology of RA. Permeability of the intestinal barrier allows for food components or bacterial endotoxins to enter the bloodstream. Absorption of endotoxins into circulation can trigger a systemic inflammatory response.
Kim et al. observed that a vegan diet lowers the relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae in the gut, which in turn reduces fecal lipocalin-2 (Lcn-2), a sensitive biomarker of intestinal inflammation, within 28 day
Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Critical appraisal
Efficacy and safety of hydroxychloroquine sulphate in rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial--an Indian experience
P - One hundred and twenty-two patients with RA were enrolled
I - 61 patients were randomized to receive either hydroxychloroquine tablets, two tablets of 200 mg daily
C - 61 patients received placebo two tablets daily.
After 8 weeks all patients received one tablet of hydroxychloroquine 200 mg daily for 4 weeks. Every patient also received one tablet of Nimesulide 100 mg twice daily.
O - 40.4% of patients on hydroxychloroquine showed improvement by modified ACR response criteria whereas only 20.7% ( p = 0.02) showed improvement in the placebo group. No significant side effects were observed in any of the patients. There were no ocular toxicities.
Obesity is implicated in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) development, severity, outcomes, and treatment response.
The independent effects of overweight and obesity on ability to achieve sustained remission (sREM) in the 3 years following RA diagnosis.
P - 982 patients
315 (32%) had a healthy BMI, 343 (35%) were overweight, and 324 (33%) were obese; 355 (36%) achieved sREM within 3 years.
O - Compared to healthy BMI, overweight patients and obese patients were significantly less likely to achieve sREM.
Rates of overweight and obesity were high (69%) in this early RA cohort. Overweight patients were 25% less likely, and obese patients were 47% less likely, to achieve sREM in the first 3 years, despite similar initial disease-modifying antirheumatic drug treatment and subsequent biologic use.


.jpeg)

.jpeg)








No comments:
Post a Comment